Introduction to RVSM
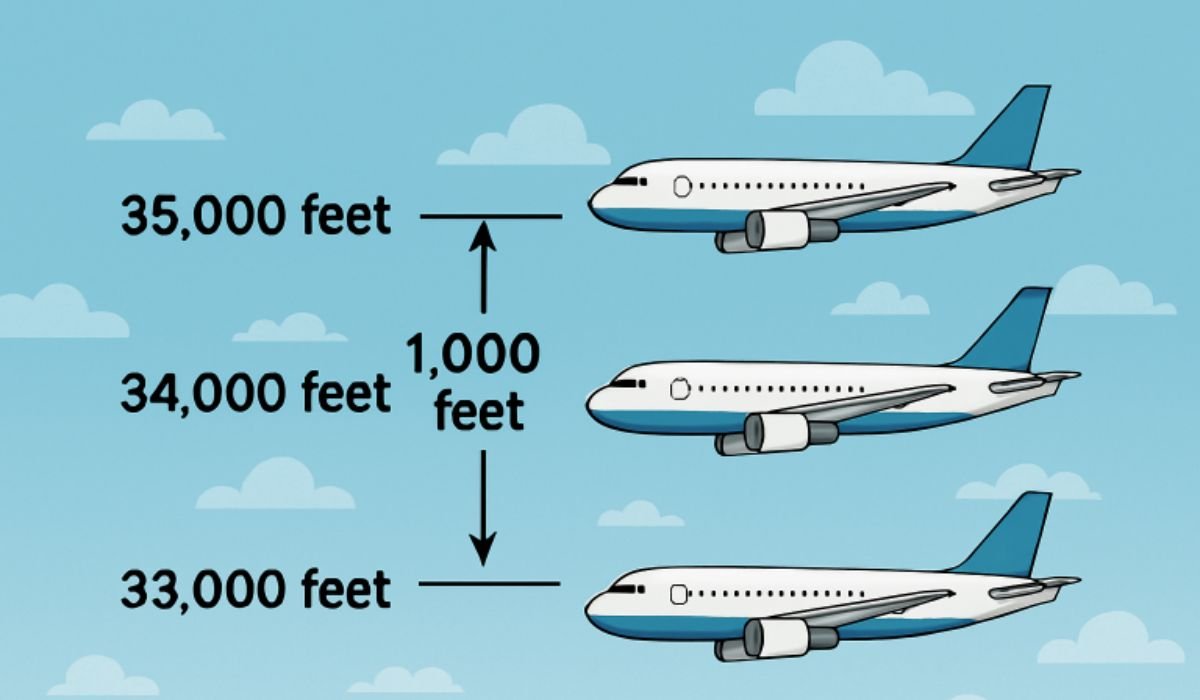
Reduced Vertical Separation Minimum (RVSM) is a global aviation standard that allows aircraft to fly with just 1,000 feet of vertical separation, instead of the previous 2,000 feet requirement, specifically within the airspace bracket of Flight Level 290 (29,000 feet) to FL 410 (41,000 feet). The primary objective behind the introduction of RVSM was to leverage advances in aircraft navigation and altitude-keeping precision, which enable more airplanes to safely share high-demand upper airspace levels. Enhanced air traffic management and operational economics are direct results of this modernization.
RVSM airspace offers a significant operational advantage for commercial and private operators seeking to maximize efficiency at cruising altitudes. Ensuring compliance with the standard requires dedicated RVSM certification for both aircraft and operators, underscoring the industry’s commitment to safety and regulatory oversight.
Millions of flights annually benefit from RVSM, as it enables more aircraft to access the altitudes where jet engines operate most efficiently, resulting in measurable fuel savings and reduced environmental impact. The FAA and ICAO have continually updated RVSM procedures to adapt to new technologies, supporting the drive for globally harmonized airspace operations.
It is crucial for aviation professionals to understand the requirements and operational protocols of RVSM, given their direct impact on flight planning, compliance, and in-flight safety. Operators with approved aircraft and crews can leverage RVSM to optimize routes and reduce operational costs, thereby reinforcing the sector’s drive for both efficiency and sustainability.
Historical Background
Prior to the adoption of RVSM, aircraft above FL290 had to maintain a vertical separation of 2,000 feet, primarily due to historical limitations in altimeter and avionics technology that made precise altitude keeping at high altitudes challenging. As air travel grew, the demand for optimal cruise levels in the increasingly crowded skies strained available capacity, prompting the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) to establish review panels exploring more efficient options. The 1988 Review of the General Concept of Separation Panel concluded that, with modern technology, a 1,000-foot separation was not only feasible but also safe for widespread adoption—a standard subsequently adopted worldwide throughout the 1990s and early 2000s. You can learn more about the history and rationale behind this shift in this FAA resource on RVSM.
Implementation and Certification
The implementation of RVSM requires a holistic approach that encompasses aircraft equipment, crew training, and ongoing compliance monitoring. Aircraft must feature dual, independent altitude-measurement systems, altitude alerting systems, capable autopilots, and encoding transponders. Operators must secure approval from regulators—often following a comprehensive evaluation that includes equipment installation, altitude keeping performance, crew training, and maintenance procedures. Thorough documentation and periodic revalidation underpin the ongoing certifications for RVSM implementation globally. Even after approval, operators remain subject to routine audits and must promptly address any deviations to maintain current validation.
Benefits of RVSM
The operational improvements introduced with RVSM are far-reaching. The most direct benefit is the significant increase in airspace capacity; more aircraft can safely maintain optimal, fuel-efficient cruising altitudes simultaneously. Airlines and corporate operators have realized substantial cost savings from reduced fuel burn and shorter, more direct routes at these altitudes. Additionally, the environmental advantage—lower emissions from jet aircraft—is supported by global agencies as a meaningful contributor to sustainable aviation. According to the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the combined effect of improved fuel efficiency and time savings positions RVSM as a central pillar for modern, economically sound airspace management.
Safety Considerations
Despite the dramatic reduction in vertical spacing, RVSM maintains a rigorous safety margin through strict technical and procedural protocols. Regulatory authorities, such as the FAA, emphasize that only aircraft and flight crews with full RVSM approval may enter RVSM airspace, unless explicitly permitted under specific circumstances. Continuous performance monitoring—including Large Height Deviation (LHD) reporting programs and in-service data analysis—helps detect and remedy anomalies before they compromise safety. Non-compliant aircraft are rapidly cleared out of RVSM-designated airspace, sustaining high safety standards throughout heavily trafficked regions.
Technological Advancements
Modern avionics advancements underpin the implementation and ongoing success of RVSM. Enhanced dual altimeters, advanced autopilot systems, and transponders ensure highly accurate adherence to flight levels. Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast (ADS-B) technology now enables real-time monitoring of aircraft positions and altitude in RVSM airspace, streamlining both real-time surveillance and incident post-mortem analysis. Further developments—such as geometric altimetry—are being considered by programs like SESAR in Europe to enable even finer airspace management and potentially allow for even more reduced separation standards in the future.
Global Adoption
The success of RVSM hinges on its universal adoption and standardization. ICAO’s global framework facilitated phased implementation across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Africa. Each region established surveillance and safety assessment programs, such as the Asia-Pacific Approvals Registry and Monitoring Organization (APARMO), to oversee compliance and integrity of operations. These efforts are complemented by regular data sharing, joint safety assessments, and adaptation to regional airspace complexities.
Future of RVSM
Looking ahead, the evolution of RVSM is continuing to be shaped by global collaboration and the rapid pace of technological advancements. The SESAR Joint Undertaking and other international research bodies are actively studying the feasibility of reducing vertical separation to just 500 feet at cruising altitudes, contingent upon further advancements in navigational accuracy and in-service monitoring technologies. These possibilities promise to further increase airspace capacity, efficiency, and sustainability benchmarks, ensuring RVSM remains at the forefront of safe and efficient global air traffic management. With a firm foundation of data-driven monitoring, cross-border cooperation, and ongoing investment in avionics, the future of RVSM heralds more streamlined, environmentally conscious, and economically efficient skies.
RVSM stands out as one of the most significant advancements in aerospace, enabling operators to combine safety with efficiency in the modern era. Continued attention to regulatory compliance and technological innovation ensures that RVSM remains a cornerstone of effective airspace use worldwide.