Understanding Hard Water and Its Effects
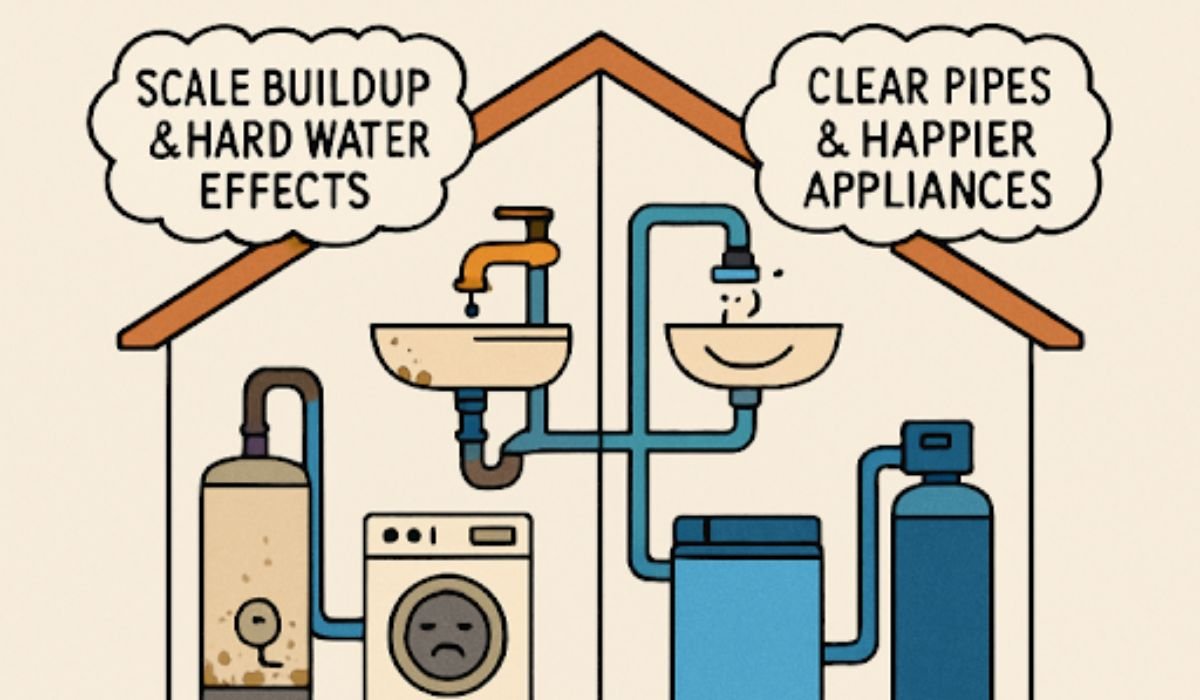
Many households face issues with hard water, which contains elevated levels of calcium and magnesium. Over time, these minerals can accumulate as scale in pipes and appliances, lowering plumbing efficiency, damaging water heaters, and reducing the lifespan of your appliances. These mineral deposits also impact how effectively soap lathers, resulting in wasted detergent and potential skin discomfort for some residents. If you notice stiff laundry, spotty dishes, or dry skin after showers, hard water could be affecting your home. Addressing challenging water problems is essential for both household health and comfort.
Residents who want to improve their water quality often start by exploring water softeners Tampa for reliable whole-house solutions. Whole-house water softening systems are designed to treat all the water entering your home, providing benefits far beyond just drinking or cooking.
Types of Whole-House Water Softeners
There are primarily two categories of whole-house water softeners that homeowners should consider:
- Salt-Based Ion Exchange Softeners: These systems are the industry standard for effectively softening water. They work by exchanging hard minerals (primarily calcium and magnesium) in the water with sodium ions. Regular maintenance involves replenishing the salt supply and periodic system checks. These units are known for their ability to significantly reduce limescale and extend the life of appliances that use water regularly.
- Salt-Free Water Conditioners: Rather than removing minerals, salt-free conditioners alter the structure of these minerals so they do not adhere to surfaces and form scale. These systems require less maintenance and are friendlier to the environment because they do not discharge brine. However, their effectiveness can diminish in areas with extremely high mineral concentrations.
Understanding the differences between these types will help you select a system that fits your home’s needs and complies with local regulations. Both systems have advantages, but your choice should depend on your water hardness, environmental priorities, and maintenance preferences.
For a more in-depth explanation of the science behind water softening technologies, consider reading resources such as the U.S. Geological Survey’s Water Science School page, which explains hard water minerals and their impact on daily life.
Key Features to Consider
Choosing a water softener involves more than simply addressing hard water. Homeowners should assess several core features to ensure lasting performance and value:
- Regeneration Method: Modern softeners use demand-initiated regeneration, which triggers cleaning cycles only when necessary. This increases efficiency by reducing water and salt consumption compared to systems on a fixed schedule.
- Salt Efficiency: Efficient models use less salt and water during regeneration. Opting for salt-efficient units saves money and reduces environmental impact.
- Additional Filtration: Some whole-house softeners are paired with multi-stage filtration, removing iron, sediment, and chlorine to improve taste and further protect appliances.
- Innovative Technology: Newer systems offer Wi-Fi connectivity for remote monitoring, allowing homeowners to track water usage or receive maintenance alerts directly on their devices.
By considering these features, you gain not only consistently softened water but also optimized operations and maintenance, which translates into greater comfort and cost savings.
Certifications and Water Quality Testing
To ensure both performance and safety, select a water softening system that has earned certifications from organizations such as the NSF (National Sanitation Foundation) or WQA (Water Quality Association). Certification verifies that manufacturers’ claims about durability, efficacy, and safety are backed by independent, industry-standard testing. For homes using well water, conducting a comprehensive water quality test before purchase is also highly recommended. Testing reveals the specific mineral content in your supply, helping you choose the most suitable system and guiding future maintenance or upgrades. The EPA’s guide on private wells offers excellent tips for getting started with water testing.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
While some water softener kits can be installed with basic plumbing skills, professional installation is the best route for reliability, efficiency, and compliance with warranty terms. Installation tasks often include integrating the system into your main water line, setting up drain lines, and calibrating timers or electronic controls. Ongoing maintenance for most units centers on monitoring salt or conditioner levels and, occasionally, cleaning tanks to prevent residue buildup. Opting for systems known for low-maintenance operation can save considerable time and effort year over year.
Environmental Impact
Salt-based water softeners discharge brine, or salty wastewater, into local sewer systems during regeneration. In large quantities, chlorides from this discharge can accumulate in rivers and lakes, posing a threat to aquatic life and water quality. In response, several municipalities have imposed restrictions or outright bans on salt-based softeners. If you are an environmentally-conscious homeowner or live in an area with such regulations, it is wise to consider alternative water conditioning technologies or confirm compliance with local laws before installation. Resources like Scientific American’s coverage on water softening and environmental impact provide greater insight into regulatory developments and best practices.
Cost Implications and Long-Term Benefits
While whole-house water softeners represent a significant upfront investment, the long-term value can be substantial. Initial costs cover the unit, installation, and basic setup, while regular maintenance may involve salt replenishment and periodic system checks. However, these expenditures are typically offset by reduced repair costs, longer appliance lifespans, lower energy consumption, and enhanced comfort in daily routines. Many homeowners report significant savings on maintenance and improved efficiency of water-driven appliances, validating the investment over several years.
Conclusion
Making the right choice for a whole-house water softener depends on fully understanding your water composition, comparing technologies, and honestly assessing priorities such as environmental impact and long-term maintenance. By selecting the right unit for your household and following best practices for installation and care, you can protect your home, lower utility bills, and enjoy softer, healthier water for years to come.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: Practical Fireplace Installation Tips for Modern Homes