Healthy trees are not only essential for curb appeal and property value, but also play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance. To prevent costly landscape damage, recognizing tree diseases in their earliest stages is crucial. Whether you’re a homeowner or property manager, cultivating a proactive approach to tree health helps avert large-scale issues. If you need expert advice or services locally, consider landscape repair Fort Wayne, IN.
Many diseases can be managed or even reversed when they are detected before extensive damage occurs. Vigilant observation, paired with swift action, gives your trees the best chance at a healthy life span. Learning to spot the warning signs ensures your landscape remains vibrant throughout the year. Healthy trees are also vital for supporting wildlife, reducing energy costs, and enhancing the overall resilience of urban and suburban environments.
READ ALSO: Cultivating a Healthy Urban Forest: Tips for Homeowners and Communities
Recognizing Early Symptoms
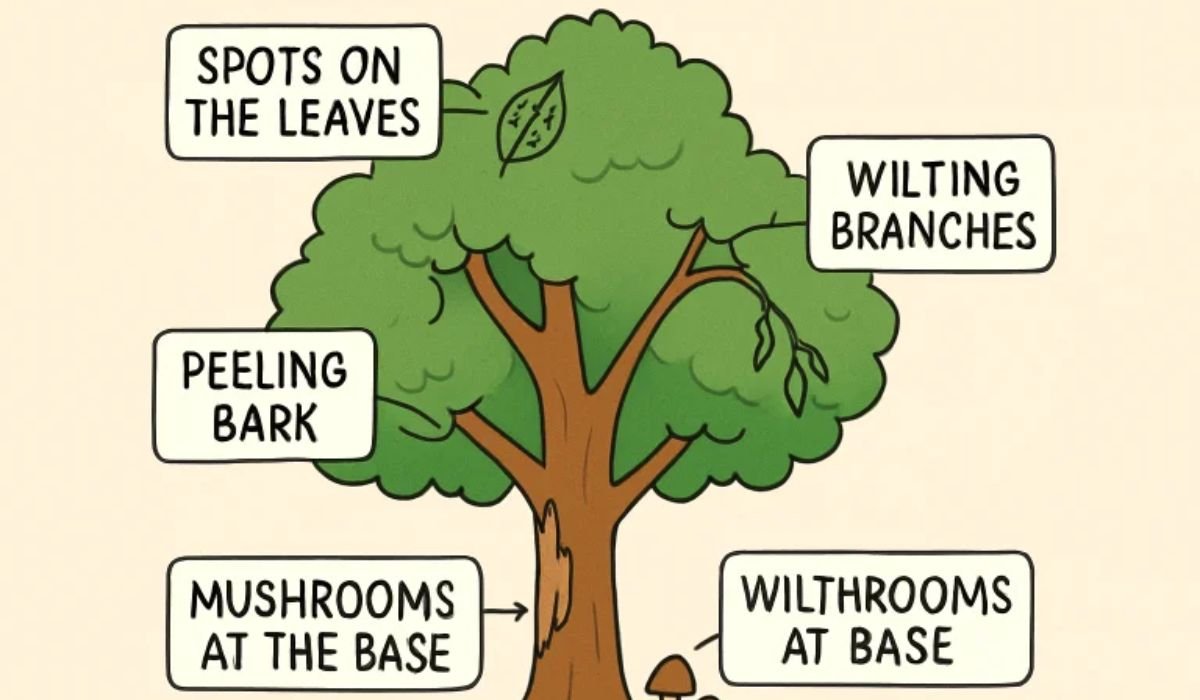
Spotting the onset of disease symptoms early is the best protection for your landscape. Typical clues of distress include:
- Leaf Discoloration and Spots: Yellow, brown, or black patches are often initial indicators of fungal infections, such as anthracnose or leaf spot diseases. Any unusual mottling on leaves should be inspected.
- Bark Abnormalities: Flaky or peeling bark, deep fissures, or oozing sap can point to fungal or bacterial disease. Sometimes, a sour odor is present.
- Wilting or Premature Leaf Drop: Roots infected with pathogens often can’t provide enough moisture, causing the tree to shed leaves early or wilt unexpectedly.
- Unusual Growths or Fungal Presence: Mushrooms at the base signal possible heartwood rot. Swellings called galls can result from both biological infections and insect invasion.
Common Tree Diseases and Their Indicators
Anthracnose
Anthracnose is a fungal disease that is prevalent in cool, wet weather, particularly in the spring. It appears as tan, black, or brown spots on leaves and can also cause twigs to deform. Early detection prevents severe defoliation in susceptible trees, such as sycamore, dogwood, and maple. Infected leaves may curl or drop prematurely, reducing the tree’s vigor.
Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew appears as a dusty white or gray coating on leaf surfaces. It’s more visible during periods of high humidity, but does not require water-saturated leaves to spread. While not usually fatal, it can weaken a tree’s defenses and decrease its ability to photosynthesize, impacting species such as oak, maple, and fruit trees.
Dutch Elm Disease
This devastating vascular disease, spread primarily by elm bark beetles and root grafts, leads to wilting and gradual yellowing of leaves. Symptoms often begin in the upper branches and progress downward, ultimately causing dieback and tree death if not managed promptly. The American Elm is especially vulnerable, making early intervention essential.
Preventive Measures
Vigilance and proper care practices are your best defenses against tree disease. Fundamental steps include:
- Regular Inspections: Monthly visual checks from spring through fall help you spot subtle changes before they escalate. Inspections are crucial after storms or periods of high rainfall.
- Proper Pruning: Remove weak, dead, or infected branches. Always disinfect pruning tools between cuts to prevent the spread of pathogens. Make clean cuts at the branch collar to aid healing.
- Soil Management: Fertilizing based on annual soil testing ensures trees remain well-nourished. Mulch at a depth of 3-4 inches helps regulate moisture, buffers roots from temperature swings, and reduces weed competition. Avoid piling mulch against the trunk to prevent rot.
- Watering Practices: Deep, infrequent watering—preferably in the morning—encourages the development of deep roots and helps trees withstand drought. Overwatering promotes fungal growth and shallow root development. Adjust the frequency according to the season and local rainfall.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you notice that symptoms persist or worsen, or if your tree shows advanced signs such as large patches of dead bark, widespread leaf drop, or conks (fungal bodies) on the trunk, it’s time to consult a certified arborist. Tree health professionals utilize diagnostic tools and laboratory testing to ensure accurate identification and can then customize an effective management or removal strategy. Acting quickly can often save a valuable tree and protect others nearby from the spread of disease.
Final Thoughts
Consistent vigilance, a proactive care schedule, and professional support, when needed, are the building blocks for robust, disease-resistant trees. By learning the key symptoms and best practices outlined here, you’ll secure the long-term beauty and health of your landscape.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: The Benefits of Regular Tree Health Inspections