Many facility managers and homeowners overlook the importance of proper maintenance for HVAC systems, leading to inefficiencies and higher energy costs. Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) plays a crucial role in optimizing HVAC performance, enhancing efficiency, and extending equipment lifespan. By implementing a consistent PPM schedule, individuals can identify potential issues before they develop into costly repairs.
Regular maintenance tasks, such as cleaning filters and inspecting ductwork, not only improve air quality but also reduce energy consumption. HVAC systems in top condition operate more effectively, which can result in noticeable savings on utility bills. By prioritizing PPM, facilities can maintain indoor comfort while simultaneously being environmentally conscious.
Understanding the benefits of PPM empowers facility managers and homeowners to take proactive measures. Investing in a planned approach to HVAC maintenance ultimately fosters a reliable and efficient system that serves its purpose effectively for years to come.
Fundamentals of HVAC Systems
A thorough understanding of HVAC systems is crucial for optimizing their performance. This includes knowledge of the main components and the significance of regular maintenance in enhancing efficiency.
HVAC Components and Functions
HVAC systems consist of several key components, each playing a vital role.
- Heating Unit: This could be a furnace or heat pump that warms the air.
- Ventilation: This involves the exchange of indoor and outdoor air to ensure fresh air circulation.
- Air Conditioning: This unit cools and dehumidifies indoor air.
- Ductwork: This is responsible for distributing air throughout the property.
These components work together to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Proper sizing and design of each part are essential for optimal functionality.
Importance of Maintenance in HVAC Efficiency
Regular maintenance of HVAC systems is essential for maximizing their efficiency.
- Filter Replacement: Dirty filters can hinder airflow, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Inspections: Routine checks can identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Cleaning Components: Dust and debris can impede system performance.
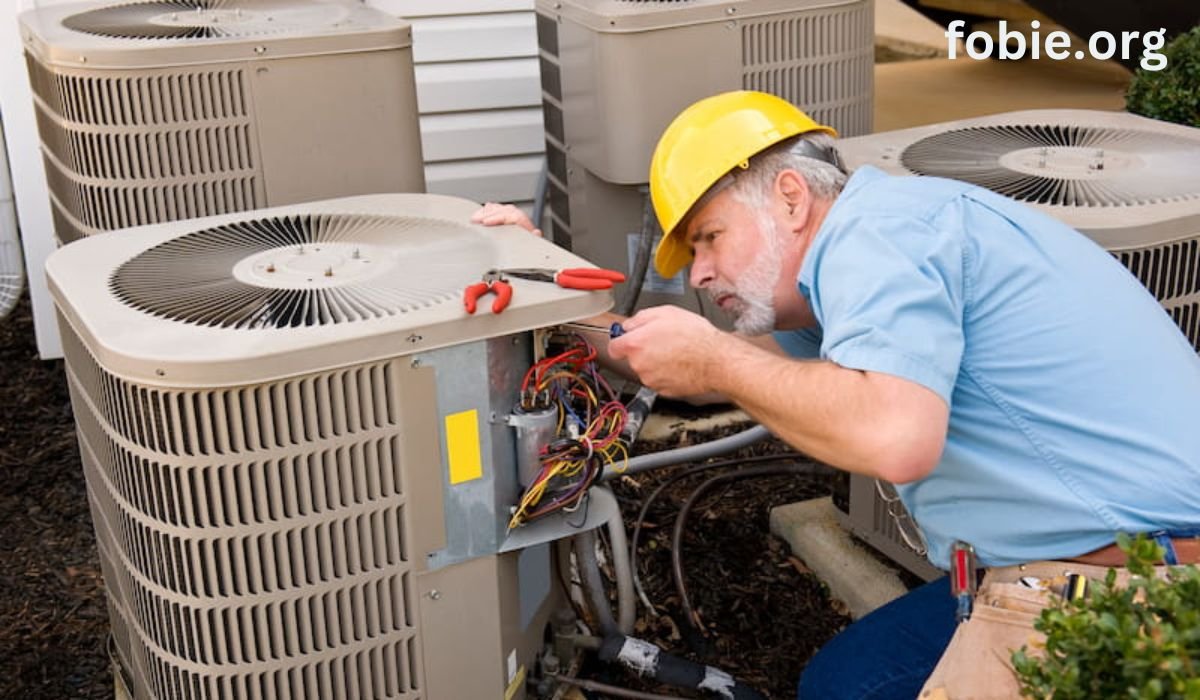
By implementing a Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) strategy, property owners can ensure their HVAC systems operate effectively. This approach not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also reduces energy costs.
Strategies for PPM of HVAC Systems
Implementing effective strategies for Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) is crucial for optimizing HVAC systems. The following approaches enhance reliability, improve energy efficiency, and extend the lifespan of essential equipment.
Scheduling and Planning Preventative Maintenance
Establishing a comprehensive maintenance schedule is vital. It should include regular inspections, cleanings, and replacements based on the manufacturer’s recommendations. Utilizing software tools can help create detailed scheduling calendars, facilitating tracking of maintenance tasks.
Routine assessments allow for identifying potential issues early. Strategically planning maintenance during off-peak hours minimizes disruption. Prioritizing critical components in need of more frequent care can optimize resource allocation.
Document all maintenance activities for reference. This provides insights into system performance over time, allowing for adjustments to the maintenance plan as necessary.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
PPM strategies contribute significantly to energy efficiency. Regular maintenance ensures that HVAC systems operate at peak performance, reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
Filtration checks are essential; cleaning or replacing filters improves airflow and efficiency. Ensuring thermostat settings are accurate helps maintain consistent temperatures without excess energy use.
For long-term savings, consider retrofitting older systems with modern technology. Upgrading to programmable thermostats or variable speed drives can enhance operational efficiency, directly impacting energy costs.
Investing in maintenance extends equipment life, resulting in fewer costly replacements. Establishing a clear budget for PPM can lead to increased overall savings for facilities.
Common Preventative Maintenance Procedures
Common procedures in PPM include various tasks aimed at ensuring HVAC functionality.
- Filter Replacement: Change filters every 1-3 months or as needed.
- Cleaning Coils: Ensure evaporator and condenser coils are free of dirt and debris.
- Checking Refrigerant Levels: Maintaining proper refrigerant levels is crucial for efficiency.
- Inspecting Ductwork: Look for leaks or blockages that can hinder airflow.
- Lubricating Moving Parts: Greasing motors and bearings can reduce wear and energy use.
Implementing these procedures can prevent major breakdowns and enhance system reliability. Regular maintenance fosters an environment where HVAC systems function optimally, ensuring comfort and efficiency year-round.
Implementing PPM in Different Climates
Implementing Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) requires tailored strategies depending on the climate. For HVAC systems, extremes in temperature can greatly influence maintenance schedules and procedures.
Adaptations for Extreme Cold
In regions with extreme cold, HVAC systems need specific adaptations to maintain efficiency and functionality. Regular checks on heating equipment are vital, focusing on components like furnaces and boilers, as they can struggle to perform under harsh conditions.
Key Actions include:
- Insulation Inspection: Ensure that pipes and ductwork are properly insulated to prevent heat loss.
- Filter Maintenance: Condensing units in extreme cold may require more frequent filter changes to avoid blockage.
- Routine Checks: Conduct inspections before winter months, including airflow tests and thermostat functionality checks.
Implementing these measures helps prevent breakdowns and ensures optimal heating performance.
Challenges in Hot and Humid Environments
In hot and humid climates, HVAC systems face different hurdles, particularly regarding cooling efficacy and energy consumption. High temperatures can increase strain on AC systems, leading to potential failures if not properly maintained.
Key Considerations include:
- Drainage System Maintenance: Regular checks on condensate drains are crucial to prevent water damage and mold growth.
- System Calibration: Adjusting systems for humidity levels can enhance efficiency. High humidity requires balancing cooling and dehumidification.
- Energy Audits: Scheduled energy assessments help identify areas for efficiency improvements, such as upgrading outdated components.
These steps ensure that systems operate effectively in challenging conditions and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Effective monitoring and continuous improvement are essential for optimizing HVAC systems through Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM). These practices ensure that systems operate at peak efficiency and adapt to changing conditions.
Performance Metrics and Benchmarks
Key performance metrics provide a quantifiable way to evaluate HVAC system efficiency. Metrics like energy consumption, temperature consistency, and humidity levels are crucial.
Benchmarks can be established by comparing current performance against historical data or industry standards. For instance, an HVAC system’s energy usage may be assessed against the Energy Star ratings.
Tracking these metrics allows for quick identification of underperforming systems, enabling timely interventions.
A well-structured dashboard can display these metrics for easy monitoring. Regular analysis of this data supports informed decision-making and helps to keep maintenance schedules aligned with actual system performance.
Feedback Loops and System Adjustments
Feedback loops facilitate ongoing communication between the HVAC system’s performance and maintenance team. This process involves collecting data from various sensors and user inputs to understand how well the system meets its intended goals.
When discrepancies occur, timely adjustments are made based on the feedback received. For example, if temperature readings exceed set parameters, adjustments can be made to the system’s settings or equipment.
Regular meetings to discuss findings from feedback loops further enhance system efficiency. Keeping all parties updated ensures that all maintenance efforts are aligned with operational goals.
Creating a culture of continuous improvement means always looking for ways to enhance performance, whether through updated technology or refined processes.